The Model-View-Controllor design pattern in PHP
Written by
Yoann Pigné
Document original
on
Document original
on

This work by Yoann Pigné is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Prerequisite
A few needed technologies
- HTTP
- REST
- Security
Hypertext Transfer Protocol
Application-level protocol for distributed systems. Generic and stateless.
- Request message (from client to server)
- Response message (from server to client)
- Text-based messages / Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) format
- Messages
generic-message = start-line *(message-header CRLF) CRLF [ message-body ] start-line = Request-Line | Status-Line
HTTP Headers and Entities
message-header = field-name ":" [ field-value ]
field-name = token
field-value = *( field-content | LWS )
field-content = <the OCTETs making up the field-value
and consisting of either *TEXT or combinations
of token, separators, and quoted-string>Example request headers and entities
Host: tools.ietf.org
Connection: keep-alive
Cache-Control: max-age=0
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8
Accept-Encoding: gzip,deflate,sdch
Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.8
Accept-Charset: UTF-8,*;q=0.5
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_8_2) AppleWebKit/537.17 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/24.0.1312.57 Safari/537.17
HTTP Requests
From the client to the server
Request = Request-Line
\*(( general-header
| request-header
| entity-header ) CRLF)
CRLF
[ message-body ] Request Line
Request-Line = Method SP Request-URI SP HTTP-Version CRLF
HTTP Methods
"OPTIONS": information about the communication options available"GET": retrieve whatever information is identified by theRequest-URI"HEAD": same as"GET"message-bodyin the response"POST": append entity to the existingRequest-URI"PUT": store entity as the newRequest-URI"DELETE": delete existingRequest-URI"TRACE": see what is being received at the other end of the request chain"CONNECT": for use with a proxy that can dynamically switch to being a tunnel (e.g. SSL tunneling).
HTTP Responses
Response = Status-Line
*(( general-header
| response-header
| entity-header ) CRLF)
CRLF
[ message-body ]
Status-Line = HTTP-Version SP Status-Code SP Reason-Phrase CRLF
Status Codes
1xx: Informational - Request received, continuing process2xx: Success - The action was received, understood, and accepted3xx: Redirection - Further action must be taken to complete the request4xx: Client Error - The request contains bad syntax or cannot be fulfilled5xx: Server Error - The server failed to fulfill an apparently valid request
Representational State Transfer
REST is a style of software architecture for distributed systems on top of HTTP.
- Each resource are accessed through one unique request (URI).
- Requests are stateless (identification within the URI)
- Resources are accessed one by one or as collections
- RESTful web service (RESTful web API)
RESTful Web Services
RESTful API and HTTP methods
| Resource | GET | PUT | POST | DELETE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collection URI | List elements | Replace entire collection | Create new element in collection | Delete collection |
| Element URI | Retrieve one element | Replace existing element | *Generally not used* | Delete one element |
- Plural may indicate a collection e.g.
http://example.com/emails/ - An id may indicate an element e.g.
http://example.com/email/17/ - URN can be prefixed with API version e.g.
https://api.twitter.com/1.1/statuses/home_timeline.json
Security
Too many vulnerabilities exist... But developers are responsible for their code!
Common Attacks
- Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
- Cross-site scripting (XSS)
- SQL injection
Common Measures
- Anti-CSRF tokens
- Forms Timeouts
- Escape users inputs
Reduce vulnerability... Use frameworks!
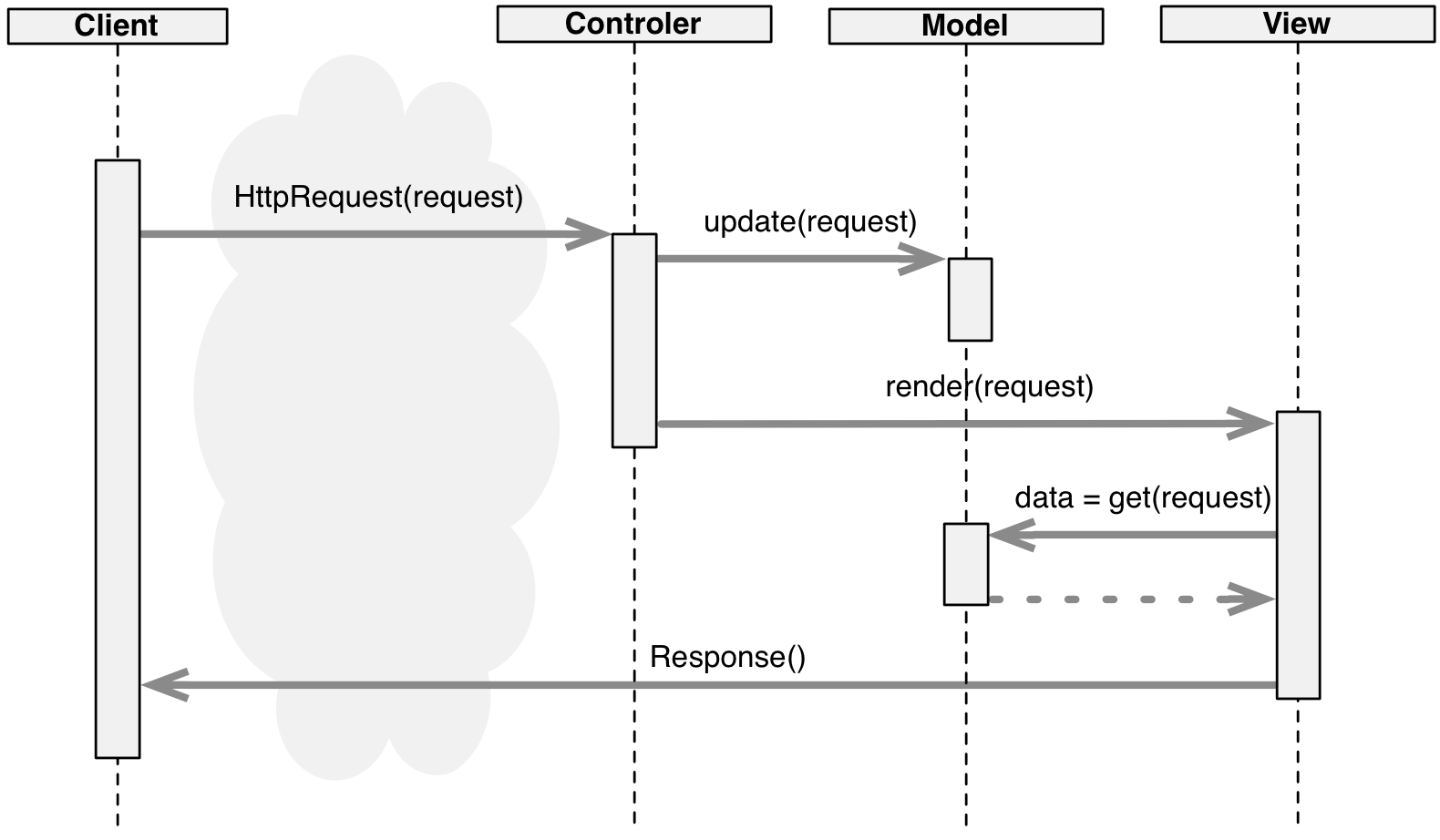
MVC
The Model–View–Controller Design Pattern
- Improve the separation of concerns
- Facilitate automated unit testing
- Facilitate team work
Model
- Holds the data
- Links to persistent storage (DBMS)
- Ignores other components
View
- Representation of data
- What users see
- May know the Model
Controller
- Handles users requests
- Updates Model data
- Triggers Views
MVC Schema
MVC Sequence
A simple PHP script
Show news and allow comments on them.
<?php
$connect = mysql_connect('myserver', 'mylogin', 'mypassword');
mysql_select_db('myDB');
if ($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] == 'POST') {
$news_id = $_POST['news_id'];
mysql_query("INSERT INTO commentaires SET news_id='$news_id',
auteur='".mysql_escape_string($_POST['auteur'])."',
texte='".mysql_escape_string($_POST['texte'])."',
date=NOW()"
);
header("location: ".$_SERVER['SCRIPT_NAME']."?news_id=$news_id");
exit;
} else {
$news_id = $_GET['news_id'];
}
?>
<!-- [...] -->
<!-- [...] -->
<html><head><title>Les news</title></head>
<body>
<h1>Les news</h1>
<div id="news">
<?php
$news_req = mysql_query("SELECT * FROM news WHERE id='$news_id'");
$news = mysql_fetch_array($news_req);
?>
<h2><?php echo $news['titre'] ?> postée le <?php echo $news['date'] ?></h2>
<p><?php echo $news['texte_nouvelle'] ?> </p>
<?php
$comment_req = mysql_query("SELECT * FROM commentaires
WHERE news_id='$news_id'");
$nbre_comment = mysql_num_rows($comment_req);
?>
<h3><?php echo $nbre_comment ?> commentaires relatifs à cette nouvelle</h3>
<?php while ($comment = mysql_fetch_array($comment_req)) {?>
<h3><?php echo $comment['auteur'] ?>
a écrit le <?php echo $comment['date'] ?></h3>
<p><?php echo $comment['texte'] ?></p>
<?php } ?>
<!-- [...] -->
<!-- [...] -->
<form method="POST" action="<?php echo $_SERVER['SCRIPT_NAME'] ?>"
name="ajoutcomment">
<input type="hidden" name="news_id" value="<?php echo $news_id?>">
<input type="text" name="auteur" value="Votre nom"><br />
<textarea name="texte" rows="5" cols="10">
Saisissez votre commentaire
</textarea><br />
<input type="submit" name="submit" value="Envoyer">
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Various actions are mixed up in this file:
- Request handling
- Database update
- Database lookup
- Visualization (style?)
- Security
- Routing
<?php
function dbconnect() {
static $connect = null;
if ($connect === null) {
try {
$connect = new PDO("mysql:dbname=simplemvc;host=127.0.0.1", 'pigne', 'n2EfCJYFx6CExzSX' );
$connect->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
} catch (PDOException $e) { echo 'Connection failed :( : ' . $e->getMessage(); exit;}
}
return $connect;
}
/* [...] */
/* [...] */
function get_news($id) {
try{
$sql = "SELECT * FROM news WHERE id= :id";
$sth = dbconnect()->prepare($sql);
$sth->execute(array(':id' => $id));
if($sth->errorCode() == 0) {
return $sth->fetch();
}
else {
return array();
}
}catch (PDOException $e) { echo 'Select comments failed: ' . $e->getMessage(); exit;}
}
function get_comments($news_id) {
try {
$sql = "SELECT * FROM commentaires WHERE news_id= :news_id";
$sth = dbconnect()->prepare($sql);
$sth->execute(array(':news_id' => $news_id));
if($sth->errorCode() == 0) {
return $sth->fetchAll();
}
else {
return array();
}
}catch (PDOException $e) { echo 'Select comments failed: ' . $e->getMessage(); exit;}
}
/* [...] */
/* [...] */
function insert_comment($comment) {
$connect = dbconnect();
try{
$sql = "INSERT INTO commentaires SET news_id= :news_id , " .
"auteur= :auteur , " .
"texte= :texte , " .
"date=NOW()";
$sth = $connect->prepare($sql);
$sth->execute(array(':news_id' => (int)$comment['news_id'],
':auteur' => $connect->quote($comment['auteur']),
':texte' => $connect->quote($comment['texte']),
)
);
} catch(PDOException $e) { echo 'Insert failed: ' . $e->getMessage(); exit;}
}
The View
<html><head><title>Les news</title></head>
<body>
<h1>Les News</h1>
<div id="news">
<h2><?php echo $news['titre'] ?> postée le <?php echo $news['date'] ?></h2>
<p><?php echo $news['texte_nouvelle'] ?> </p>
<h3><?php echo $nbre_comment ?> commentaires relatifs à cette nouvelle</h3>
<dl>
<?php foreach ($comments AS $comment) {?>
<dt><?php echo $comment['auteur'] ?>, le <?php echo $comment['date']?>:</dt>
<dd><?php echo $comment['texte'] ?></dd>
<?php } ?>
</dl>
<h3>Un commentaire ?</h3>
<form method="POST" action="<?php echo $_SERVER['SCRIPT_NAME'] ?>" name="ajoutcomment">
<input type="hidden" name="news_id" value="<?php echo $news['id']?>">
<input type="text" name="auteur" placeholder="Votre nom"><br>
<textarea name="texte" placeholder="Saisissez votre commentaire"></textarea><br>
<input type="submit" name="submit" value="Envoyer">
</form>
</div>
</body></html>
The Controller
require ('simpleModel.php');
if ($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] == 'POST') {
insert_comment($_POST);
header("HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently");
header("location: {$_SERVER['SCRIPT_NAME']}?news_id={$_POST['news_id']}");
exit;
} else {
$news = get_news($_GET['news_id']);
$comments = get_comments($_GET['news_id']);
$nbre_comment = sizeof($comments);
require ('simpleView.php');
}
PHP MVC Frameworks
Many of them
- Agavi
- CakePHP
- CodeIgniter
- Copix
- Dynatrix
- FuelPHP
- Gest-HVSL
- Hoa
- Jelix
- Kinkama
- Kohana
- MODx
- Open Web Framework
- Postnuke
- QCodo
- Symfony
- TemplatePP
- Yii Framework
- Zend Framework
- Joomla! Platform







